rabeprazole sodium
CLINICAL USE
Gastric acid suppressionDOSE IN NORMAL RENAL FUNCTION
10–120 mg daily, doses >100 mg in 2 divided dosesPHARMACOKINETICS
DOSE IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT
GFR (mL/MIN)
DOSE IN PATIENTS UNDERGOING RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPIES
IMPORTANT DRUG INTERACTIONS
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugsADMINISTRATION
Reconstition
–Route
OralRate of Administration
–Comments
–OTHER INFORMATION
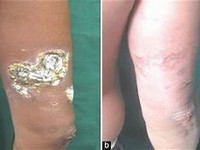
Interstitial nephritis has been reported with rabeprazole sodium.
See how to identify renal failure stages according to GFR calculation
See how to diagnose irreversible renal disease
Home